|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
When it comes to choosing a graphics card for gaming, content creation, or general computing, two names dominate the conversation: NVIDIA and AMD. Each brand offers a range of GPUs with distinct features and benefits. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between NVIDIA and AMD graphics cards to help you make an informed decision.
1. Architecture and Performance
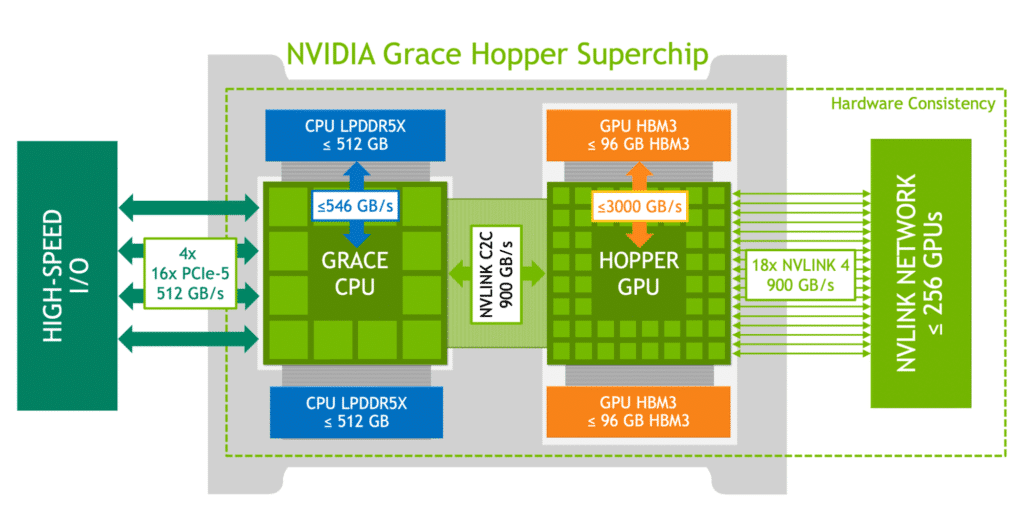
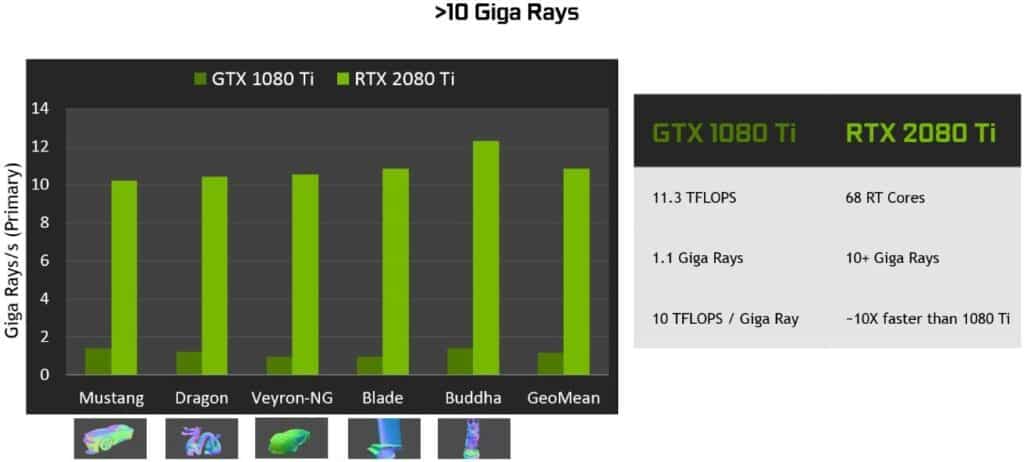
NVIDIA:
- Architecture: NVIDIA’s GPUs are built on architectures like Ampere (RTX 30 Series) and Ada Lovelace (RTX 40 Series). These architectures are known for their advanced ray tracing capabilities, AI-enhanced features, and robust performance.
- Performance: NVIDIA’s high-end cards, such as the RTX 4090, offer exceptional performance in gaming, 3D rendering, and AI tasks. They are often praised for their efficiency in ray tracing and DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling), which boosts frame rates by leveraging AI.
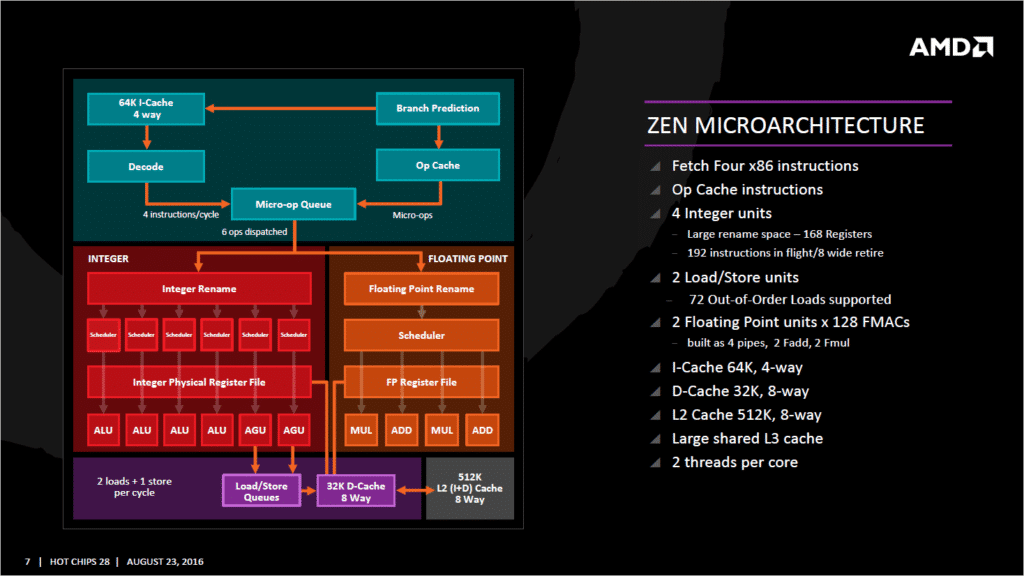
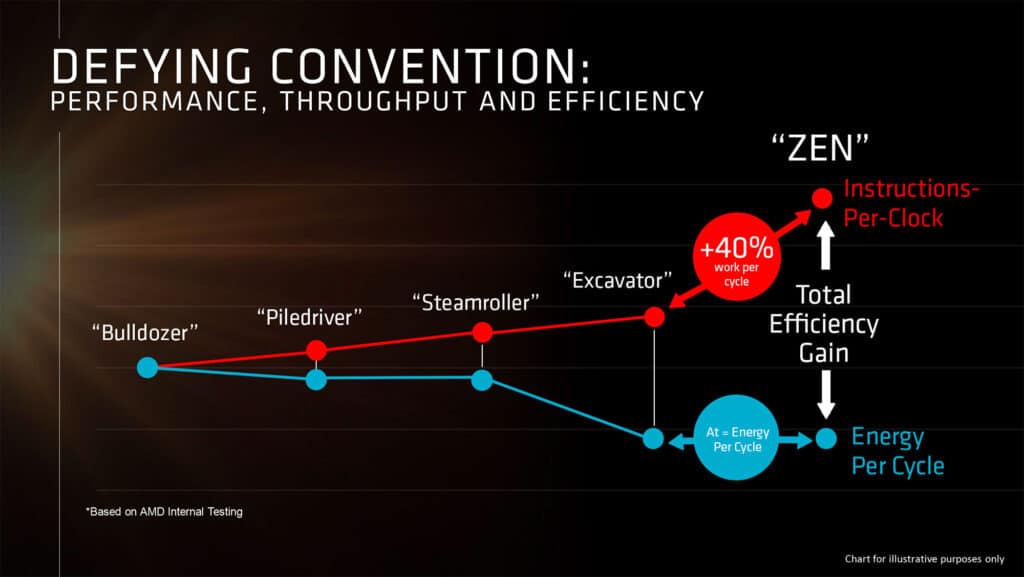
AMD:
- Architecture: AMD’s GPUs use the RDNA (Radeon DNA) architecture, with RDNA 2 (Radeon RX 6000 Series) and RDNA 3 (Radeon RX 7000 Series) being the latest. These architectures focus on improving power efficiency and delivering high performance per watt.
- Performance: AMD’s high-end GPUs, like the RX 7900 XTX, are competitive in gaming and content creation. They offer strong performance and are known for their value in terms of cost-to-performance ratio. AMD’s RDNA 3 also introduces significant advancements in ray tracing and AI capabilities.
2. Ray Tracing and AI Features

NVIDIA:
- Ray Tracing: NVIDIA leads the way in ray tracing technology, providing advanced lighting and shadow effects in supported games. Their RTX cards include dedicated RT (Ray Tracing) cores that handle these complex calculations efficiently.
- DLSS: NVIDIA’s DLSS technology uses AI to upscale lower-resolution images to higher resolutions, improving performance while maintaining image quality. This feature is available in a growing number of games and is a significant advantage for NVIDIA users.

AMD:
- Ray Tracing: AMD’s latest GPUs offer ray tracing support, but their performance in this area traditionally lags behind NVIDIA’s offerings. However, AMD continues to improve ray tracing capabilities with each new architecture.
- FSR: AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) is a technology similar to DLSS that enhances frame rates by upscaling lower-resolution images. FSR 2.0 and 3.0 aim to compete with DLSS by offering improved performance and image quality.
3. Software and Driver Support
NVIDIA:
- Software: NVIDIA provides robust software support through the GeForce Experience app, which offers driver updates, game optimizations, and additional features like screen recording and streaming.
- Driver Support: NVIDIA’s drivers are generally reliable and updated frequently, ensuring compatibility and performance improvements for the latest games and applications.
AMD:
- Software: AMD’s Radeon Software offers a suite of features for tweaking performance, monitoring hardware, and enhancing gaming experiences. It includes tools for overclocking, driver updates, and more.
- Driver Support: AMD has made significant strides in driver stability and performance. The company’s Adrenalin drivers are regularly updated to address issues and enhance compatibility with new games.
4. Price and Value
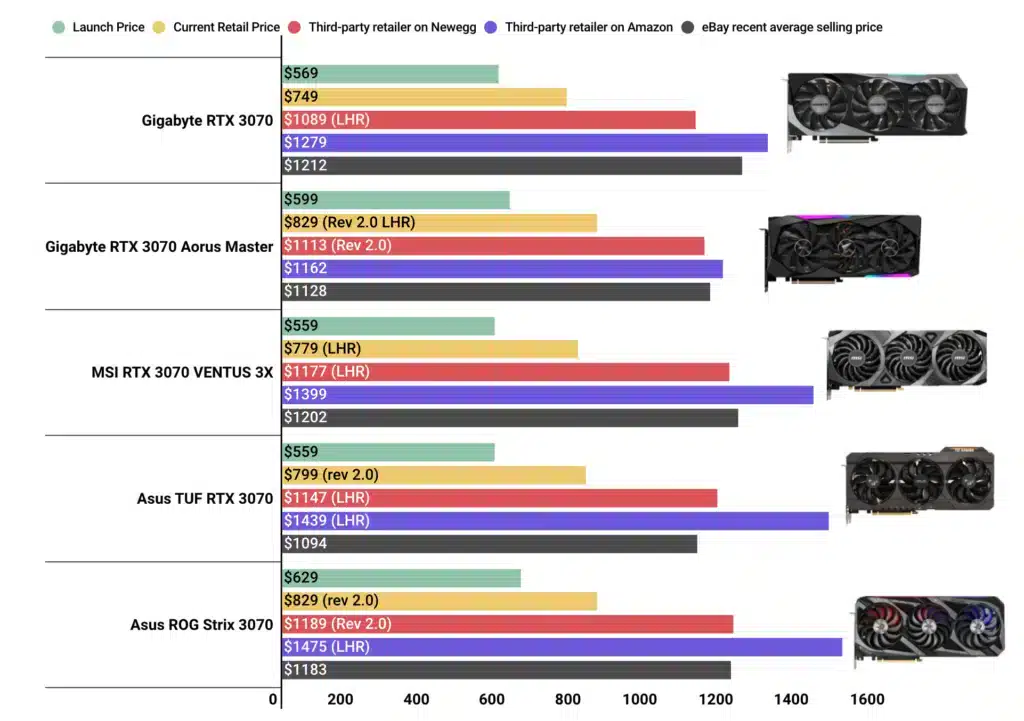
NVIDIA:
- Price Range: NVIDIA’s GPUs are often positioned in the premium segment of the market. While they offer top-tier performance, their high-end models come with a higher price tag.
- Value: NVIDIA cards tend to be pricier but are valued for their cutting-edge features, such as advanced ray tracing and AI enhancements.
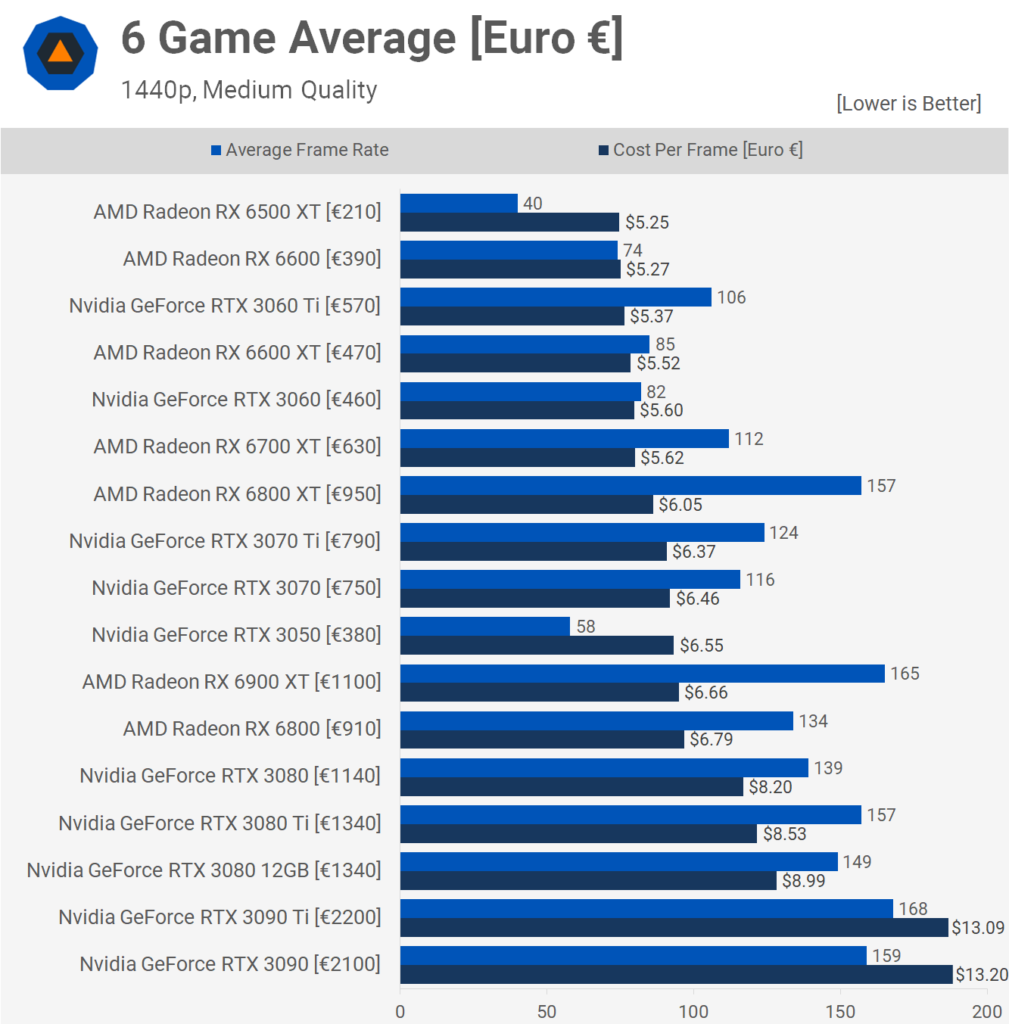
AMD:
- Price Range: AMD is known for offering competitive pricing, often providing better value for money compared to NVIDIA’s high-end options. Their GPUs are positioned to offer strong performance at a more affordable price.
- Value: AMD cards are recognized for their excellent cost-to-performance ratio, making them a popular choice for gamers and content creators looking for value.
Conclusion
Both NVIDIA and AMD offer powerful graphics cards with unique strengths. NVIDIA excels in ray tracing and AI features with technologies like DLSS, while AMD provides strong performance with competitive pricing and value. Your choice between the two will depend on your specific needs, budget, and preferences for features and performance.








